Regulatory Compliance for Pharmaceutical Vending Machines
- Introduction: Why regulatory compliance matters for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Regulatory landscape for Pharmaceutical vending machines — an overview
- Regional regulatory comparison for Pharmaceutical vending machines (US, EU, Canada, China)
- Classification and risk management for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Pharmacy practice and controlled substances: practical rules for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Data protection & cybersecurity requirements for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Cold chain and product integrity controls for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Software validation, traceability, and serialization in Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Operational controls and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Validation, documentation, and audit readiness for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Checklist: Pre-deployment considerations for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Vendor evaluation: choosing compliant Pharmaceutical vending machines
- How IMT’s Pharmaceutical vending machines align with regulatory needs
- Why choose IMT for Pharmaceutical vending machine deployments
- Implementation scenarios and practical controls for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Practical tips to stay inspection-ready for Pharmaceutical vending machines
- FAQ — Frequently Asked Questions about Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Contact and next steps — see IMT Pharmaceutical vending machines
- Sources and references
Introduction: Why regulatory compliance matters for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Pharmaceutical vending machines are transforming access to medicines in hospitals, workplaces, retail locations, and remote sites. Because these units handle medications — sometimes prescription or temperature-sensitive products — operators and manufacturers must meet a complex web of regulations covering product safety, pharmacy practice, data protection, device quality, and cybersecurity. This article explains the regulatory landscape, practical compliance steps, and how to evaluate vendors and equipment to ensure safe, legal deployment.
Regulatory landscape for Pharmaceutical vending machines — an overview
Pharmaceutical vending machines sit at the intersection of pharmaceutical law, medical device rules, pharmacy practice acts, and data/privacy regulations. Whether a machine is legal and how it must be configured depends on four main dimensions: 1) the legal status of the drugs dispensed (OTC vs prescription vs controlled substances); 2) device classification as a medical device in some jurisdictions; 3) data processing and patient privacy requirements; and 4) quality systems for temperature control, traceability and recall readiness. Operators must analyze these domains before deployment.
Regional regulatory comparison for Pharmaceutical vending machines (US, EU, Canada, China)
Requirements vary by jurisdiction. The table below summarizes common regulatory touchpoints to help teams understand differences when planning multi-country deployments.
| Region | Prescription allowed? | Serialization / Anti‑counterfeit | Data protection | Medical device / Software rules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Often restricted; depends on state pharmacy law and controlled substances rules | Drug supply chain security requirements (DSCSA) apply to supply chain participants | HIPAA for patient data; state privacy laws | FDA guidance on medical device cybersecurity and software — potential regulatory scrutiny |
| European Union | Varies by member state; many allow prescription dispensing only via authorized pharmacies/telepharmacy | Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) — serialization and safety features | GDPR applies to personal data processing | Medical Device Regulation (MDR) may apply if device claims medical functions |
| Canada | Provincial pharmacy regulations govern dispensing — prescription vending often restricted | Traceability expectations; Health Canada oversight | PIPEDA / provincial privacy laws | Health Canada regulation of medical devices and software where applicable |
| China | Local regulations and provincial approvals; some pilots for OTC and prescription via certified systems | Increasing focus on traceability and anti-counterfeit measures | Personal information protection law (PIPL) | NMPA (medical device bureau) oversight where product functions meet device definition |
Sources for table data are listed at the end of the article.
Classification and risk management for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Start compliance by classifying the machine’s function. If the equipment performs clinical decision support, administers medicines, or actively monitors patient parameters, it could meet the definition of a medical device and trigger ISO 13485 quality system requirements, risk management (ISO 14971), and potentially pre-market submission processes. Even when not a medical device, risk management must address medication errors, temperature excursions, unauthorized access, and software failures.
Pharmacy practice and controlled substances: practical rules for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Pharmacy boards and drug enforcement agencies control how prescription and controlled drugs are dispensed. Typical requirements include pharmacist oversight, valid prescription verification (including e-prescribing rules), chain-of-custody records, secure user authentication, and controlled-substance recordkeeping. For controlled substances, many jurisdictions prohibit remote automated dispensing unless very specific safeguards and registrations are in place. Always consult local pharmacy regulators before enabling prescription or controlled substance dispensing.
Data protection & cybersecurity requirements for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Pharmaceutical vending machines often collect personal health information (PHI) — for example, patient identifiers, prescriptions, or telepharmacy consultations. In the US, HIPAA requires administrative, physical, and technical safeguards; in EU countries, GDPR controls lawful processing and cross-border transfers. Cybersecurity expectations include secure authentication, encrypted communications, patch management, and logging/auditing. The FDA and other regulators expect manufacturers to integrate cybersecurity risk management into design and to provide vulnerability management plans for devices connected to networks.
Cold chain and product integrity controls for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Temperature-sensitive medicines (vaccines, biologics, some insulin formulations) require validated storage and transport controls. Pharmaceutical vending machines must include calibrated sensors, alarmed temperature controls, redundant power options, and documented temperature mapping and validation. Follow authoritative guidance such as WHO Good Distribution Practices and CDC vaccine storage guidance when designing cold-chain capabilities and SOPs.
Software validation, traceability, and serialization in Pharmaceutical vending machines
Software that manages inventory, patient records, or dispensing decisions should be treated as regulated software if it influences patient treatment. Implement software lifecycle practices (requirements, design, verification, release) and maintain traceability matrices. For drug traceability, comply with serialization/aggregation laws (e.g., EU FMD, US DSCSA requirements for supply chain stakeholders) to allow efficient recalls and to prevent counterfeit products entering the machine.
Operational controls and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Operators must implement SOPs covering: training and credentialing of staff/operators; secure stocking and inventory reconciliation; incident and near-miss reporting; audit trails for dispensing; preventive maintenance; calibration of environmental controls; and emergency procedures for power or HVAC failures. Written agreements should define responsibilities between machine owner, pharmacist of record, maintenance providers, and software vendors.
Validation, documentation, and audit readiness for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Compliance requires documentation: design history, risk assessments, IQ/OQ/PQ validation protocols (installation/operational/performance qualification), maintenance logs, software validation artifacts, and incident records. Maintain a traceable device history file and be prepared for inspections from pharmacy boards, regulators, or auditors. Regular internal audits and supplier qualification checks reduce regulatory and business risk.
Checklist: Pre-deployment considerations for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Before deploying pharmaceutical vending machines, ensure you have completed the following checklist:
- Legal assessment: confirm whether local laws permit the intended dispensing model.
- Pharmacy engagement: secure a pharmacist of record and define clinical oversight.
- Device classification: determine if the machine/software is a regulated medical device.
- Data protection plan: map PHI flows and apply HIPAA/GDPR safeguards as needed.
- Quality systems: establish SOPs, maintenance, and calibration schedules.
- Cold chain validation: perform temperature mapping and PQ for refrigerated units.
- Supply chain traceability: implement serialization scanning and recall workflows.
- Cybersecurity: apply secure authentication, encryption, patching, and logging.
- Training: provide operator and user training materials and assessments.
- Contracts: document roles, SLAs, and incident response responsibilities.
Vendor evaluation: choosing compliant Pharmaceutical vending machines
Select vendors who can demonstrate a mature quality management system, documented validation packages, cybersecurity practices, and experience with pharmaceutical customers. Look for manufacturers with export experience and capacity to adapt to local labeling, serialization, and reporting practices. A supplier should provide integration options for pharmacy systems and offer remote monitoring, inventory management, and reliable maintenance services.
How IMT’s Pharmaceutical vending machines align with regulatory needs
Founded in 2014, IMT is committed to providing customers with customized smart vending machine solutions. IMT has an independent production plant of more than 10,000 square feet and a professional software and hardware development technical team. IMT's vending machines have functions such as automatic vending, remote monitoring, and inventory management. The main products include commercial vending equipment such as smart medical operating room behavior management, smart public health cabins, smart medicine cabinets, smart beverage vending machines, coffee vending machines, etc., and provide supporting equipment control systems, background management system software development, and related after-sales services. The products are exported to more than 100 countries and regions, including the United States, Canada, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, etc. Our vision is to become the world's leading smart vending machine manufacturer.
Why choose IMT for Pharmaceutical vending machine deployments
IMT’s experience in hardware manufacturing and integrated software development supports regulatory compliance in several ways: 1) remote monitoring and inventory management enable full audit trails and rapid recall response; 2) built-in environmental sensors and alarm systems facilitate cold-chain validation; 3) the in-house technical team can deliver customized authentication and e‑prescription integration to meet local pharmacy requirements; and 4) export experience across 100+ countries demonstrates adaptability to regional serialization and data protection rules. IMT’s product family includes Drink & Snack Vending Machine, Beauty & Nail Vending Machine, Locker Vending Machine, Coffee Vending Machine, and Pharmacy Vending Machine — each engineered for modularity, security, and serviceability to support compliance and reliable operations.
Implementation scenarios and practical controls for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Common deployment models and associated controls include:
- Hospital internal supply: machines restrict access to staff with badge authentication; integrate with hospital AD and inventory systems; controlled-substance policies enforced by pharmacist oversight.
- Retail pharmacy extension: telepharmacy kiosks combine remote pharmacist consultation with authenticated dispensing; require chain-of-custody and prescription verification workflows.
- Workplace or campus clinics: usually limited to OTC and employer-authorized medications; privacy protections and recordkeeping still required.
- Rural outreach: unattended units for essential medicines — must provide robust cold-chain, remote alerts, and clear patient instructions; local regulatory approval often required.
Practical tips to stay inspection-ready for Pharmaceutical vending machines
Maintain a living compliance binder (digital or physical) for each installation that includes validation reports, device configuration records, SOPs, training logs, incident reports, and maintenance records. Schedule quarterly reviews of logs and remote-monitoring alerts, and run annual tabletop drills for power failure, recall, or cybersecurity incidents. For multi-site programs, centralize monitoring and keep a list of local regulatory contacts and pharmacy board requirements.
FAQ — Frequently Asked Questions about Pharmaceutical vending machines
Q1: Can pharmaceutical vending machines dispense prescription medications?
A1: It depends. Many jurisdictions restrict prescription dispensing to licensed pharmacies and require pharmacist oversight. Some deployments use telepharmacy and approved workflows that permit controlled dispensing; always verify local pharmacy board rules before enabling prescription dispensing.
Q2: Are Pharmaceutical vending machines considered medical devices?
A2: Not always. If the machine or its software provides medical decision support, actively administers drugs, or impacts clinical outcomes, regulators may classify it as a medical device. Evaluate the intended use against local device definitions and consult regulatory counsel.
Q3: What cybersecurity measures are essential?
A3: Implement role-based authentication, encrypted communications (TLS), secure boot and firmware signing, timely patching procedures, logging and monitoring, and an incident response plan. Manufacturers should provide vulnerability disclosure and update mechanisms.
Q4: How should temperature-sensitive drugs be managed?
A4: Use validated refrigeration units with calibrated sensors, continuous temperature logging, alarms, backup power, and documented IQ/OQ/PQ validation. Follow WHO and CDC guidance for product-specific storage requirements.
Q5: How do I handle recalls or expired stock?
A5: Ensure serialization/lot scanning on stocking, maintain real-time inventory, and integrate automated blocking of recalled lots. Have SOPs for removal, documentation, and notification to the pharmacist of record and affected patients.
Contact and next steps — see IMT Pharmaceutical vending machines
If you are evaluating pharmaceutical vending machines for your organization, IMT can help with custom configurations that support regulatory compliance, remote monitoring, validated cold-chain solutions, and software integrations for pharmacy workflows. Visit https://www.imtvending.com/ to view products and request a consultation, or contact IMT sales to discuss validation packages, export certifications, and pilot deployments.
Sources and references
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) — Guidance on cybersecurity and medical device premarket submissions (FDA, 2014/2018)
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services — HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules
- European Commission — Falsified Medicines Directive (2011/62/EU) and Delegated Acts on safety features
- European Union — General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- World Health Organization (WHO) — Good Distribution Practices for pharmaceutical products
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) — Vaccine Storage and Handling Guidelines
- International Organization for Standardization — ISO 13485 (medical devices QMS) and ISO 14971 (risk management)
- U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) / Controlled Substances Act — recordkeeping and registration requirements
- Health Canada — Regulatory oversight for drugs and medical devices
Jewelry Vending Machines for Sale | IMT
What are the application scenarios of eyelash vending machine cost?
How to start the coffee vending machine vintage business in US ?
How Much is a Snack Vending Machine? Discover Costs & Solutions - IMT
For Factory
Can you switch according to the language of our country?
Yes, our machine has 85 national languages to switch freely.
Can you print my logo, letter & picture on the product?
Yes. We offer customized services(ODM&OEM).
What kind of payment system you have?
We use imported payment systems, bills and coins (e.g. ICT) and cashless payment systems (e.g. NAYAX).
What is the life time of your Vending Machine?
15 years at least.
For Applications
Is training support provided?
We provide free operation and maintenance training to ensure that customers can master the use of vending machines proficiently.

36 slots Small Screen Metal Keypad Drink Vending Machine
Introducing the IMT 36 Slot Small Screen Metal Keypad Drink Vending Machine. Perfect for any environment, this durable and reliable vending solution provides optimum access to beverages. Explore our range of vending machines for sale, designed to increase convenience and efficiency while improving your customers' refreshment options.

Interactive Touch Screen Vending Machines for Sale – 7.1-Inch Display, 60 Slots, Refrigerated for Drinks & Snacks
Discover the IMT 60 Slot 7.1" Screen Refrigerated Drink Snack Vending Machine, a top choice among snack vending machines for sale and drink vending machines for sale. This state-of-the-art machine offers an enhanced user experience, ensuring your business attracts more customers with every purchase.
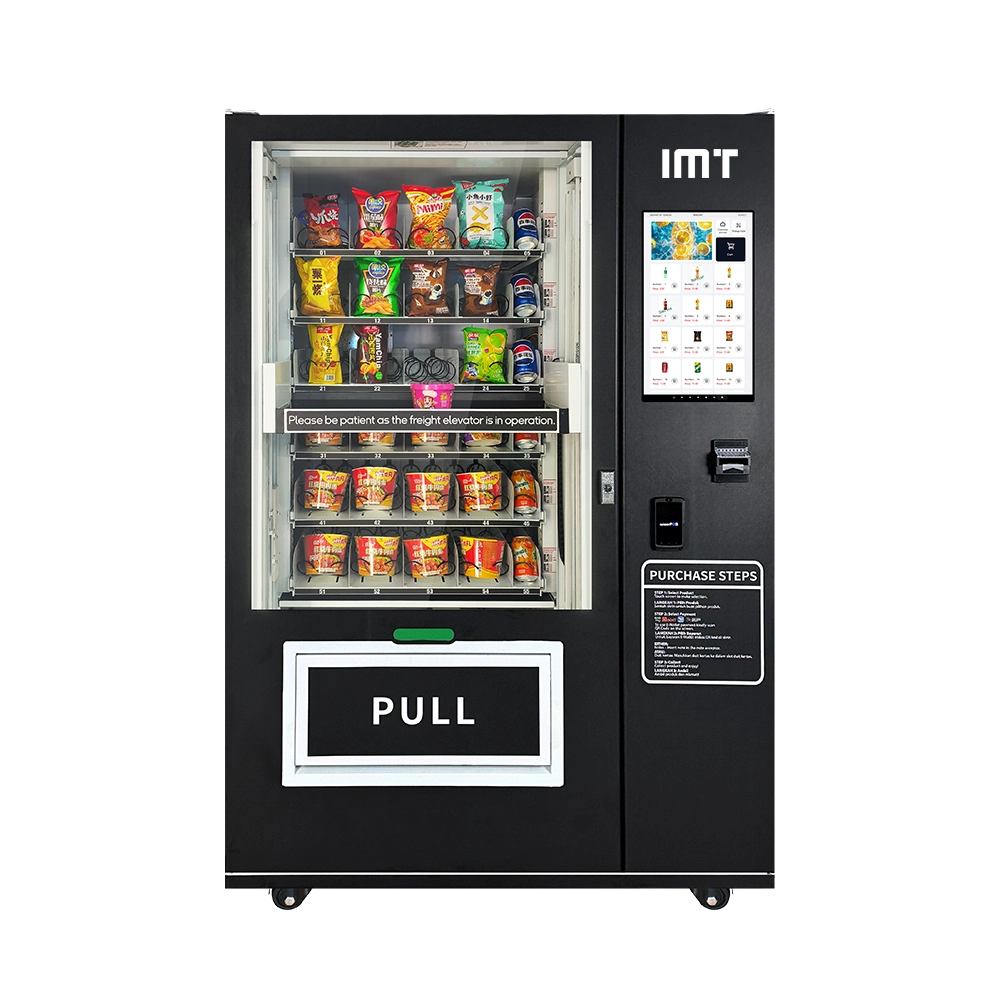

21.5-inch Screen Refrigerated Lift Drink Snack Vending Machines with Tray Elevator System
Discover the IMT 60-slot refrigerated drink and snack vending machine. Equipped with a gentle elevator delivery system that ensures product integrity, it allows you to confidently sell a wider variety of goods, including fragile items. Perfect for any location, this machine combines an interactive 21.5-inch display with reliable technology. Explore our advanced touch screen vending machines for sale today and transform your business!
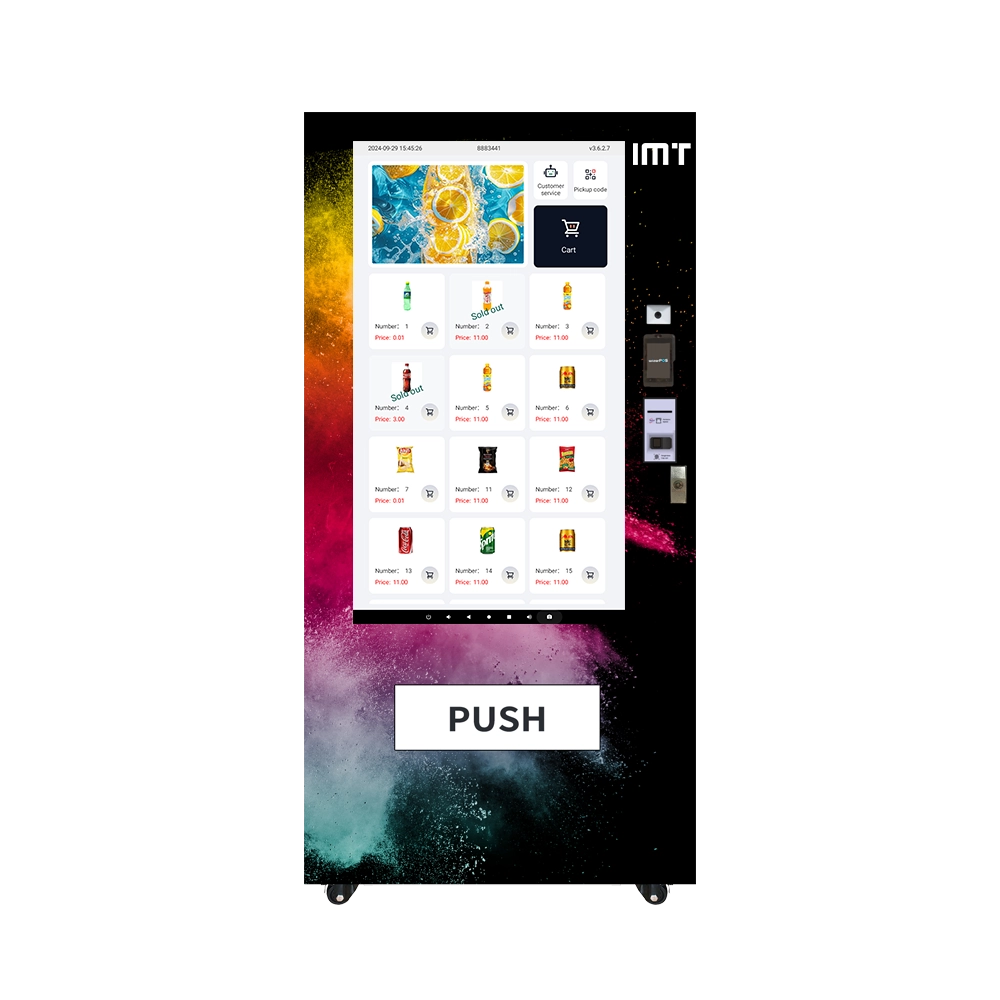
All-in-One Refrigerated Screen Vending Machine: 60 Slots for Drink & Snack
Discover the IMT 60-Slot 55-inch Screen Vending Machine for refrigerated drinks and snacks. Perfect for businesses, this machine keeps products chilled and visible on its large interactive screen. Available for sale now, it's your ultimate solution for convenience and efficiency.
© 2024 imt. All Rights Reserved.
FOLLOW US:

IMT vending Machine
IMT vending Machine
IMT Vending Machine
IMT Vending Machine